Overview
The Refugee Coordination Model (RCM) is a framework designed to ensure effective, inclusive, and accountable responses to refugee crises. It emphasizes government leadership, supported by UNHCR and a broad range of stakeholders, including local authorities, civil society, and refugee-led organizations. The model prioritizes protection, meaningful participation, and the integration of refugee responses into national systems to avoid duplication and promote sustainability. It is adaptable to diverse contexts, enabling tailored responses that address immediate needs while fostering longer-term solutions.
Central to the RCM is a collaborative, whole-of-society approach that bridges humanitarian, development, and peacebuilding efforts. The model ensures clarity in roles and responsibilities, aligning efforts across sectors and stakeholders. It promotes early engagement with development actors and integrates solutions-oriented strategies from the onset of emergencies, enabling refugees and host communities to build resilience and contribute to shared stability and growth.
Together with the UNHCR-OCHA Joint Note on Mixed Situations: coordination in practice (2014) and Serving and Protecting Together: IOM/UNHCR Framework of Engagement (2022), the RCM sets out a framework and principles for responding to both refugee and mixed situations.
Relevance for emergency operations
The Refugee Coordination Model (RCM) is relevant in emergency contexts as it provides a structured framework for organizing and streamlining responses to refugee crises, from activating the Refugee Emergency Response Scale-Up Protocol through to longer-term sustainable responses. It ensures that all actors—humanitarian organizations, governments, development partners, and local communities—work together effectively, avoiding duplication and addressing gaps. This coordinated approach enables faster, more efficient delivery of aid and protection to refugees while supporting host communities. It also facilitates joint fundraising.
By aligning efforts with national systems and integrating development actors early on, the RCM helps bridge immediate emergency responses with longer-term solutions. Its focus on protection, accountability, and meaningful refugee participation.
Main guidance
In the emergency phase of a refugee situation, the Refugee Coordination Model (RCM) provides a framework for UNHCR staff members who need to act quickly, efficiently, and in close collaboration with all relevant stakeholders. The model is a reference point to create order in what can be overwhelming circumstances and a reminder to support government leadership, diverse stakeholder engagement and the centrality of protection. Tools and resources for setting up and running the Refugee Coordination Model are available here.
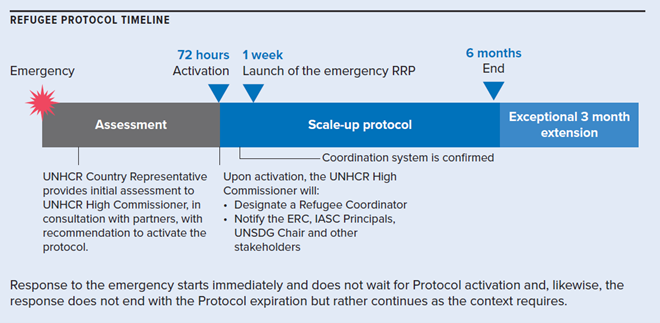
The Refugee Emergency Response Scale-Up Protocol is activated to ensure a systematic and transparent scaling-up of response capacities with clear timelines and critical steps to develop a collective response from the outset of a refugee emergency. From appointing a Refugee Coordinator (usually the UNHCR Country Representative) to establishing coordination structures within days, it streamlines the response and makes it more inclusive and predictable.
To inform the decision on activating the Emergency Refugee Response Scale-Up Protocol, within 72 hours of a refugee influx or a dramatic deterioration of the situation, the UNHCR country representative will provide the UN High Commissioner for Refugees with an initial assessment of refugee protection and humanitarian needs, and a recommendation on activating the Refugee Protocol, following inclusive consultations with response partners and relevant stakeholders. To facilitate decision-making, the initial assessment should consider scale, urgency, complexity, capacity and risk of failure to deliver effectively and at scale.
Regardless of Refugee Protocol activation, UNHCR establishes a coordination architecture that includes government, humanitarian agencies, and development partners to ensure a well-organized and comprehensive approach. The Refugee Coordination Forum (RCF) and relevant sectoral working groups should be operational within days to align efforts across humanitarian partners, governments, and local actors. Clear, inclusive leadership prevents duplication of efforts and ensures timely delivery of aid.
UNHCR’s leadership role involves setting up these coordination mechanisms, identifying priority needs, and aligning efforts to avoid duplication and maximize impact. The coordination structure should be adapted to the context and as light as possible, using existing bodies to coordinate the response where feasible.
It is critical to integrate protection principles across all sectors. During the emergency phase, UNHCR staff members must prioritize life-saving interventions while ensuring that refugee protection remains central to all actions. This includes safeguarding fundamental rights, addressing immediate risks such as gender-based violence, and ensuring access to basic services like shelter, water, and healthcare. Staff must also engage with refugees directly, ensuring their participation in decisions that affect their well-being and leveraging their insights to shape responses.
The RCM stresses the importance of aligning emergency responses with national systems and development frameworks wherever possible, planning for the transition of coordination functions and the progressive evolution of response activities. UNHCR staff are encouraged to foster partnerships with host governments, local organizations, and international actors to create responses that not only address immediate needs but also lay the foundation for longer-term resilience and self-reliance.
By embedding emergency actions within broader, sustainable strategies, UNHCR ensures that interventions contribute to durable solutions for refugees and host communities alike.
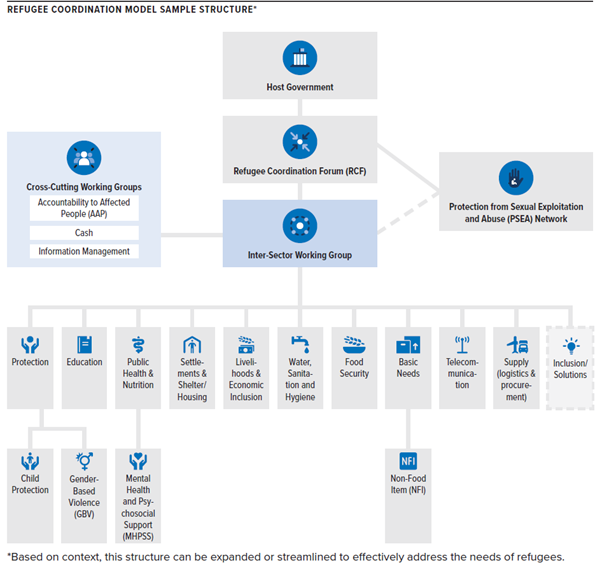
The below sample structure of the Refugee Coordination Model is for reference and so illustrates the full extent of the basic model. Most operations will require far fewer coordination groups and every operation should aim for the minimum structure possible that will still fulfil the needed coordination functions.
Post emergency phase
In the post-emergency phase, the focus shifts from immediate relief to systems- and resilience-building, and longer-term solutions. coordination structures established during the emergency should be evaluated as to whether their functions are still required given the changing needs and modes of response. Coordination groups may close, merge, or transfer their coordination functions to more sustainable mechanisms, ensuring the inclusion of local authorities, civil society and refugee-led organizations.
Although “inclusion from the start” begins with the emergency phase, it is consolidated in the post-emergency phase. As feasible, the operational response further shifts from direct provision by humanitarian actors of services and assistance (in-kind or cash) to government-led integration of refugee assistance into national systems, supported by UNHCR and partners, aligning with development goals and fostering social and economic inclusion.
Key actions in this phase include streamlining coordination groups, strengthening local system capacity, and maintaining accountability to affected populations. Risks during this phase include continued wide-scale reliance on external assistance, coordination fatigue, and failure to align with local systems.
Checklist
The Refugee Coordinator’s responsibilities:
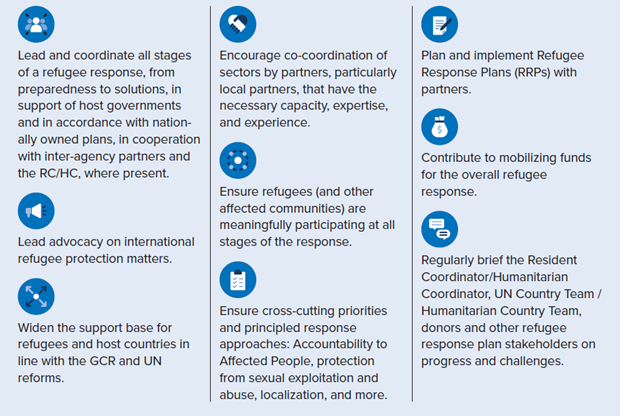
All UNHCR staff members’ responsibilities:
Setting up and running the Refugee Coordination Model in any operation takes the combined effort of all UNHCR staff members not just those that hold coordination titles or have working group chairing roles. All UNHCR staff members should consider their role in the below checklist of activities. Tools and resources for setting up and running the Refugee Coordination Model can be found on the Refugee Coordination Model Guidance website here.
- Activation and Leadership
- Activate the Scale-Up Protocol: Request the activation of the Refugee Emergency Response Scale-up Protocol, if necessary.
- Appoint Leadership: Confirm the appointment of a Refugee Coordinator to lead the response. This is usually the UNHCR country Representative or the Bureau Director for regional responses.
- Establish Coordination Forums: Set-up the Refugee Coordination Forum (RCF) and other working groups, as required. Use the sample coordination structure as a starting point but modify according to context and local needs and capacities.
- Define Roles: Clearly communicate roles and responsibilities for all stakeholders, including government, UNHCR, Resident Coordinator and/or Humanitarian Coordinator and other partners.
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Engage the Government: Coordinate with national and local authorities to align the response with existing systems and national development plans. Work with all relevant line ministries, not just the entity responsible for refugees.
- Include Diverse Stakeholders: Invite civil society, international and local NGOs, refugee-led organizations, host communities, and private-sector actors to participate.
- Foster Partnerships: Build partnerships with donors, development actors, and financial institutions to support the response.
- Needs Assessment and Planning
- Conduct Needs Assessments: Organize joint assessments to identify gaps, considering age, gender, and diversity factors.
- Develop a Refugee Response Plan (RRP): Draft and finalize the RRP in consultation with all stakeholders. The initial emergency RRP should be released within one week of the crisis start; a revised and more widely consultative and inclusive plan may be subsequently released.
- Ensure Protection Focus: Embed protection principles across all sectors, including safeguarding vulnerable groups.
- Resource Mobilization and Logistics
- Mobilize Resources: Secure funding, supplies, and technical expertise through donor engagement and partnerships. Remember, a Refugee Response Plan is a funding appeal as well as a response plan. It should be used to appeal for all participating actors, not just UNHCR.
- Set Up Logistics: Establish supply chains and pre-position critical items for rapid distribution.
- Coordinate Information Management: Set up a robust system for data collection, analysis, and sharing. Consider a 5Ws (who, what, where, when and for whom) or ActivityInfo and the Financial Tracking System.
- Operations and Monitoring
- Operationalize Coordination Groups: Ensure sector working groups and technical task forces are active and aligned with the RRP. Monitor their performance in relation to their core coordination functions, including identifying gaps and overlaps and increasing overall technical capacity.
- Maintain Two-Way Communication: Regularly consult with refugees and host communities to ensure their needs and feedback shape the response. Ensure that Accountability to Affected People (AAP) mechanisms are established and responsive.
- Monitor Progress: Track implementation, identify gaps or challenges, and adjust plans as necessary.
- Transition and Sustainability
- Plan for Transition: All sectors should map opportunities for integrating refugee assistance into national systems and development plans and track progress towards this ideal.
- Promote Durable Solutions: Collaborate on voluntary repatriation, local integration, or resettlement initiatives.
- Evaluate and Document: Assess the response, document lessons learned, and share best practices for future emergencies. Best practices can be shared on the Refugee Coordination Model guidance website here.
This checklist ensures that UNHCR staff can effectively set up and manage a coordinated, inclusive, and sustainable refugee response under the Refugee Coordination Model.
Policies, Guidelines and Useful Links
Annexes
Learning and field practices
Refugee Coordination Model guidance website, with practical tools and resources for setting up and running a refugee coordination system, including for creating and launching Refugee Response Plans.
The Inter-Agency Coordination Course (IACC), available to UNHCR staff members on Workday and to external partners here, aims to expand the competencies and skills needed to discharge leadership and coordination responsibilities across the entire forced displacement spectrum.
Links
Main contacts
Contact the Partnership and Coordination Service of the Division for External Relations:
Sara Baschetti: [email protected]
Terra MacKinnon: [email protected]
In this section:
Let us know what you think of the new site and help us improve your user experience….
Let us know what you think of the new site and help us improve your user experience….
